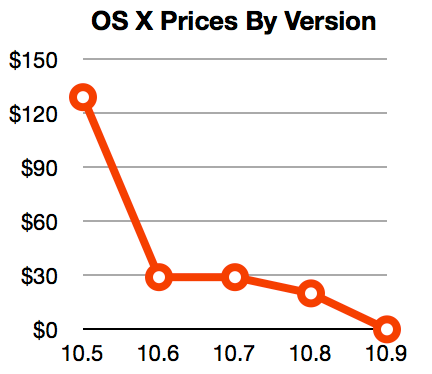
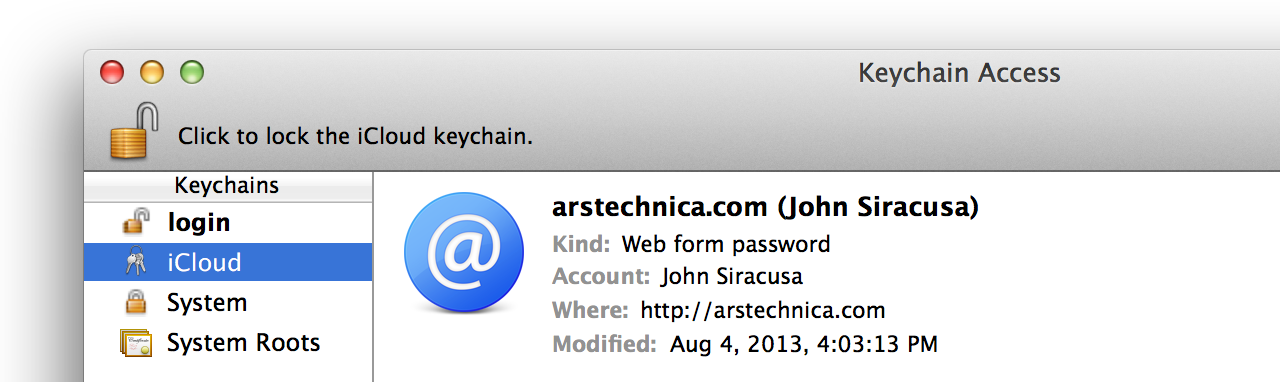
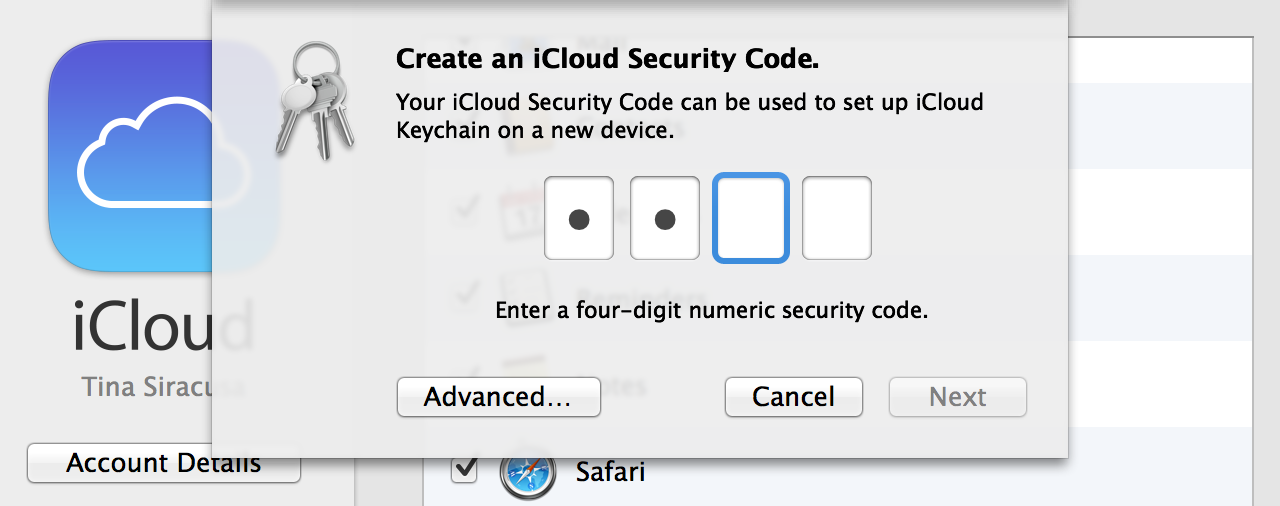
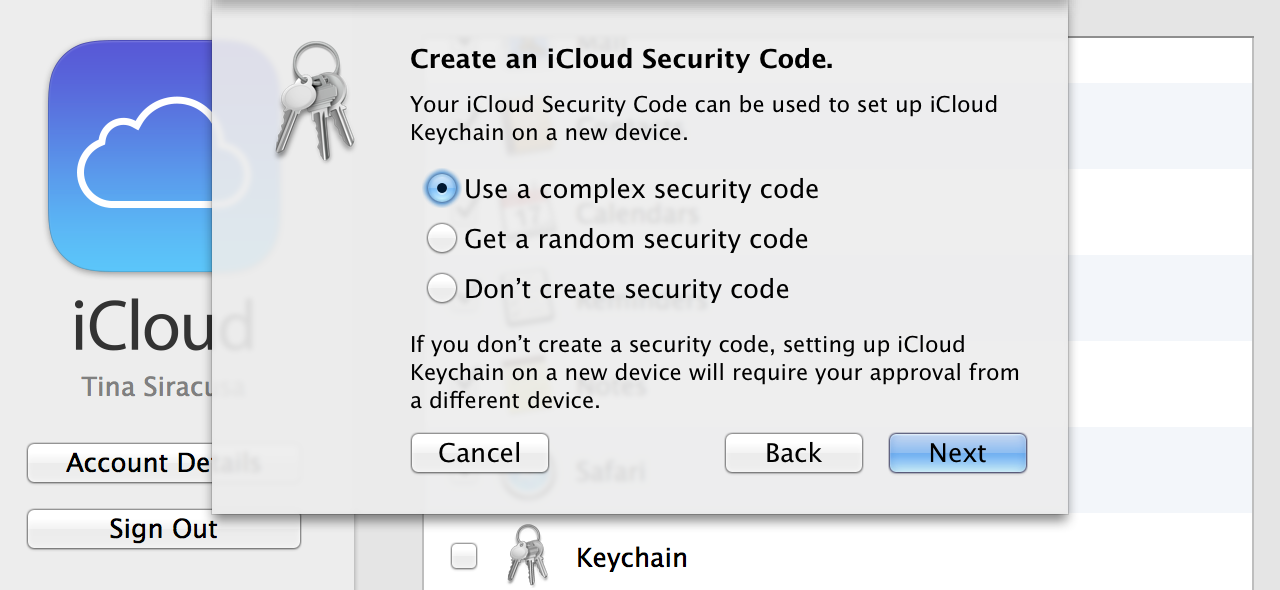
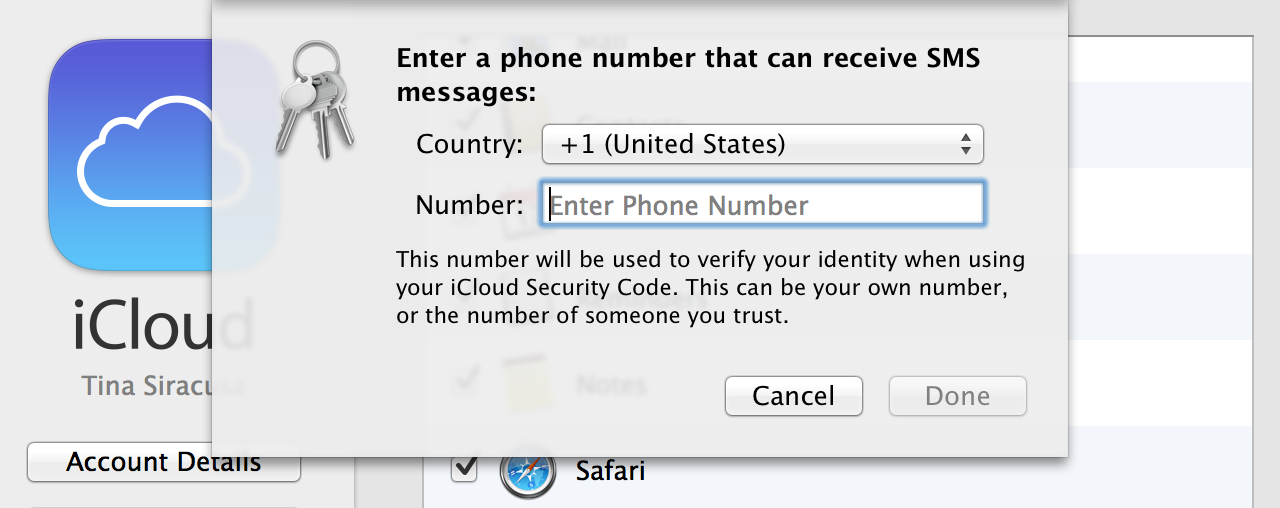
After a dozen years and nine major releases, OS X has had a full life: the exuberance of youth, gradually maturing into adulthood, and now, perhaps, entering its dotage. When I am an old operating system I shall wear… leather?
The 2011 release of OS X 10.7 Lion seemed to mark the natural endpoint of the “big cat” naming scheme. But Apple couldn’t resist the lure of the “cat, modifier cat” naming pattern, releasing OS X 10.8 Mountain Lion a year later. Perhaps it just wanted to give its cat nine lives.
The 10th major release, OS X 10.9 Mavericks, is named after an awkwardly plural California surfing spot, finally ending the feline dynasty. But what part of the operating system’s existence is this? The afterlife?
When it comes to OS X, many people are suffering from the end-of-history illusion: the belief that while the Mac platform has consistently experienced significant enhancements in the past, it will somehow not continue to grow and mature in the future.
So let’s readjust our perspective. Perhaps the first seven big-cat releases were OS X’s early childhood: birth, potty training, learning to walk and talk, and so on, culminating in some form of self-actualization.
With Lion, the Mac entered an awkward adolescence, acquiring a newfound concern about what the other kids were doing. Accordingly, OS X’s last two releases included several naked attempts to ape the look and feel of its more successful sibling, iOS.
But that was all before last year’s ouster of Scott Forstall, senior vice president of iOS Software. By all accounts, Forstall was one of the driving forces behind the iOS aesthetic that Lion and Mountain Lion so enthusiastically embraced. Jony Ive's iOS 7 strikes off in a bold new direction based on a philosophy that Apple is eager to generalize to the company as a whole—leaving OS X holding the stitched-leather bag.










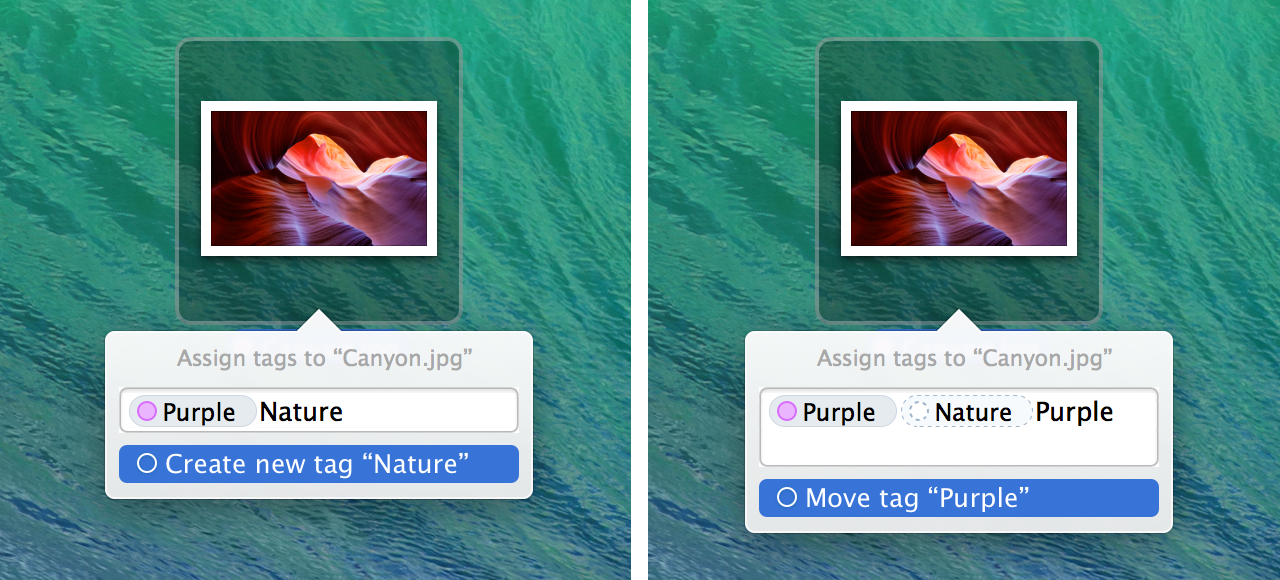
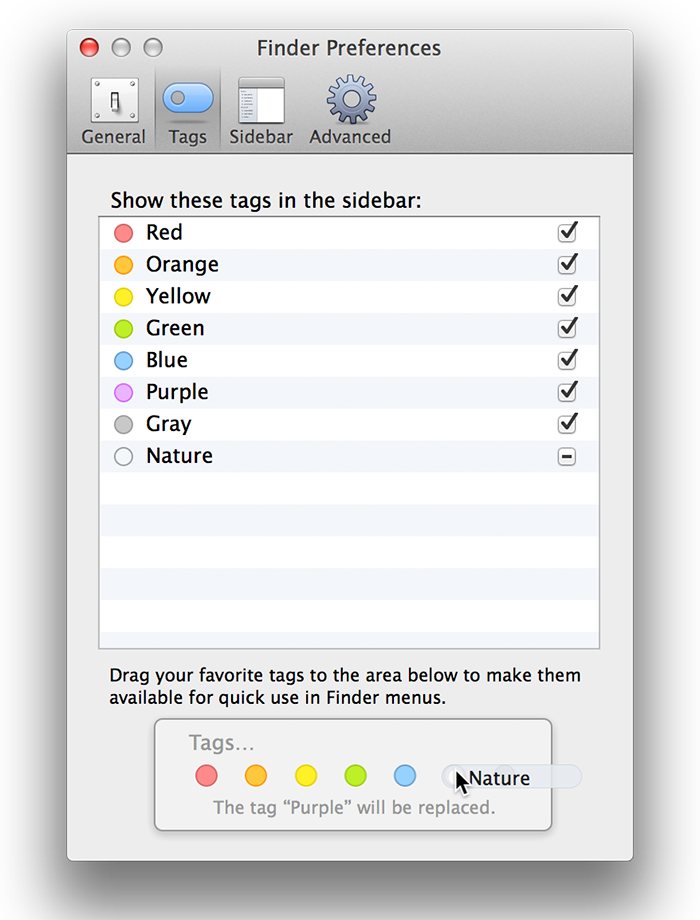
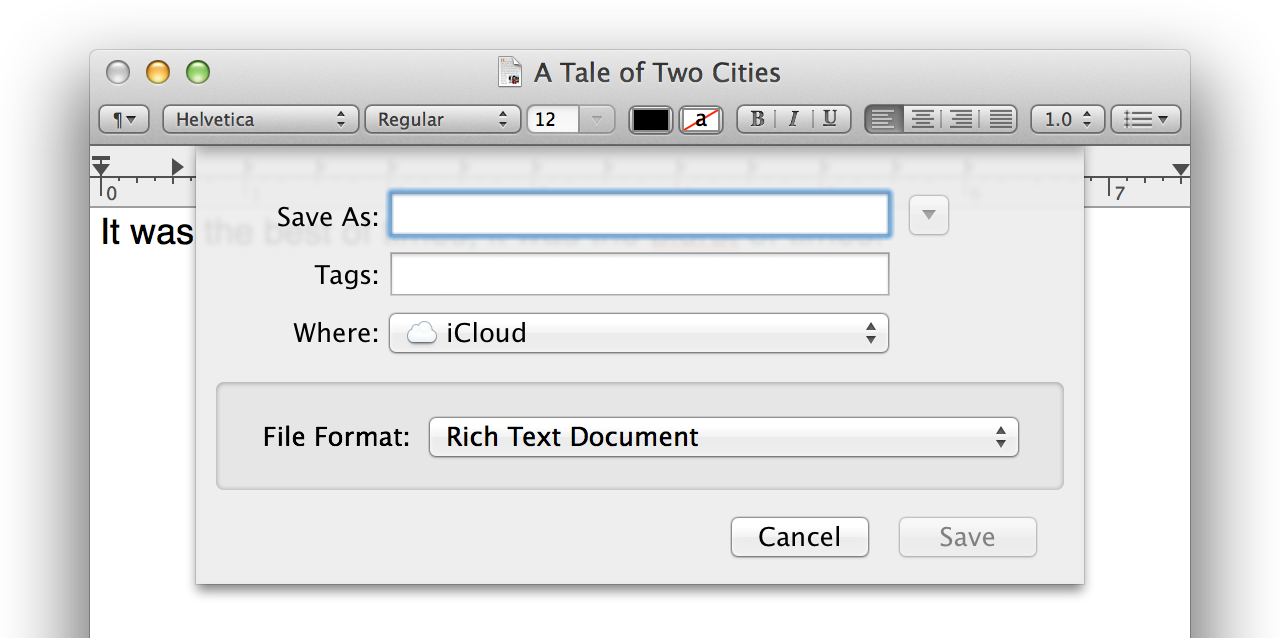



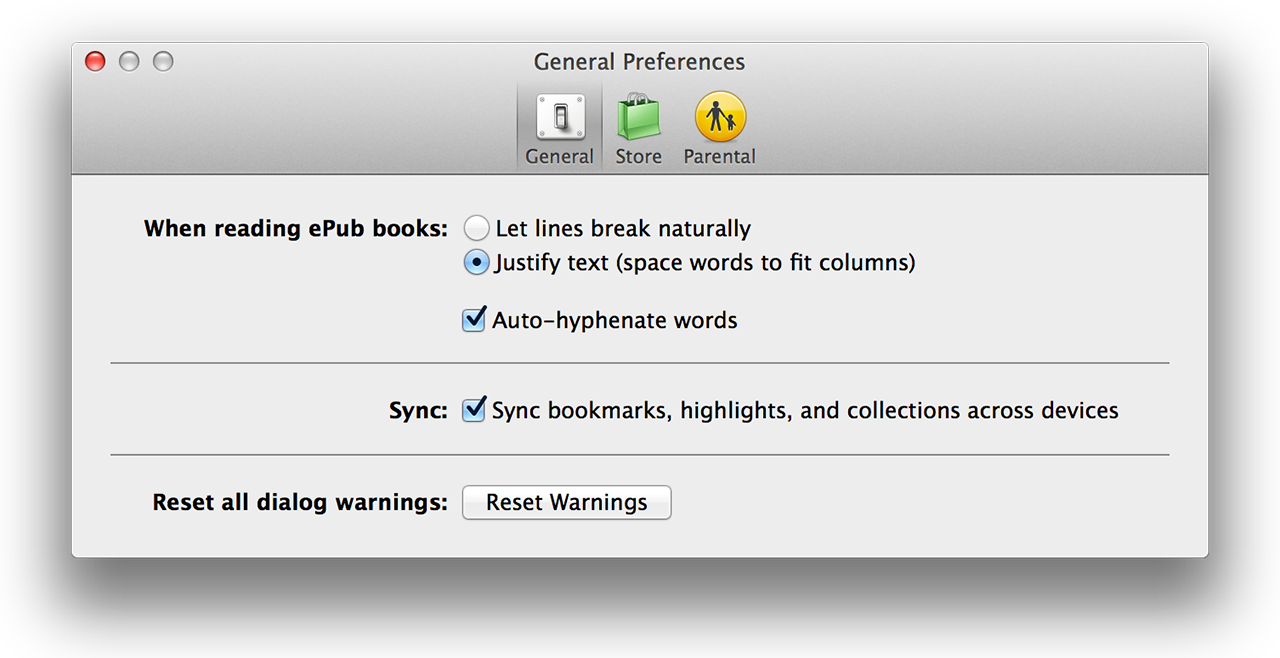


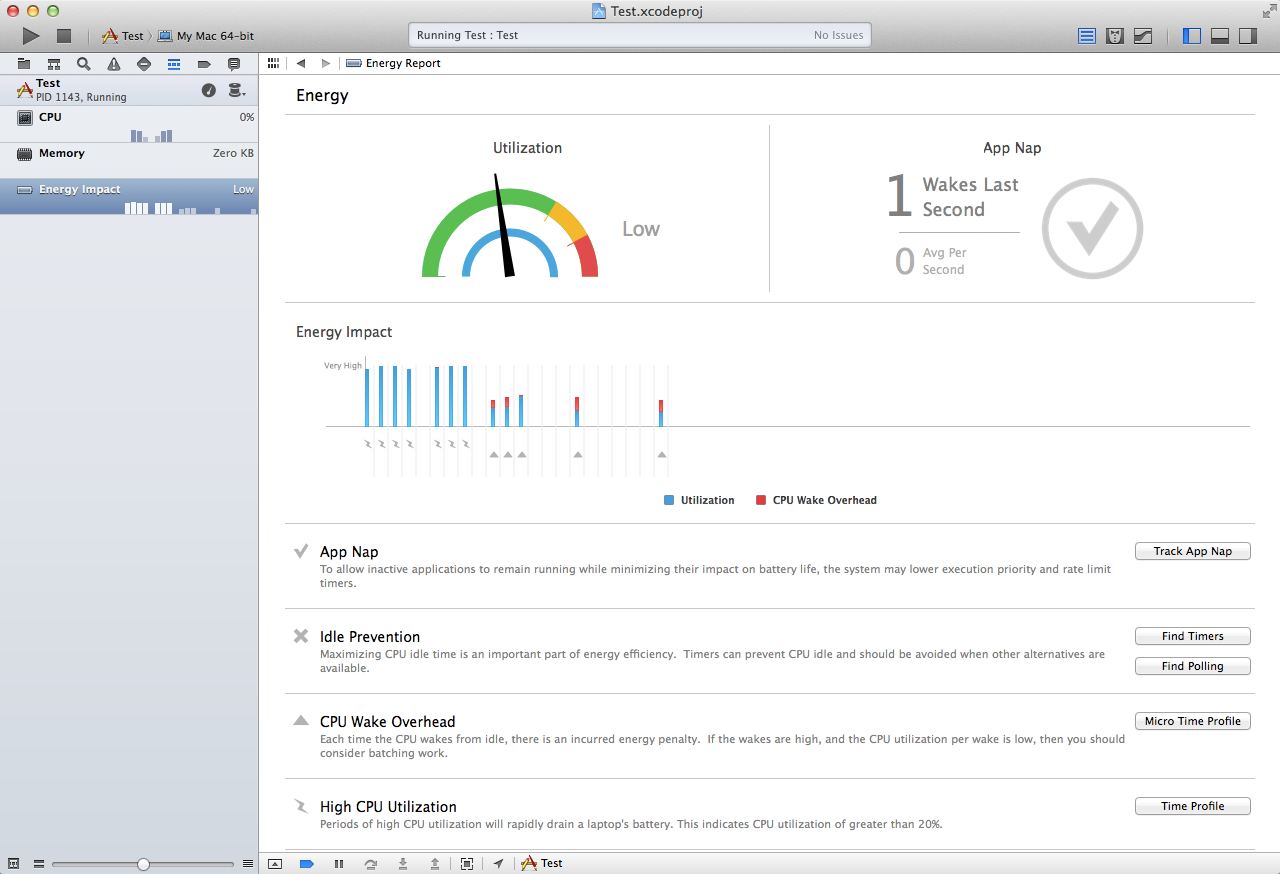
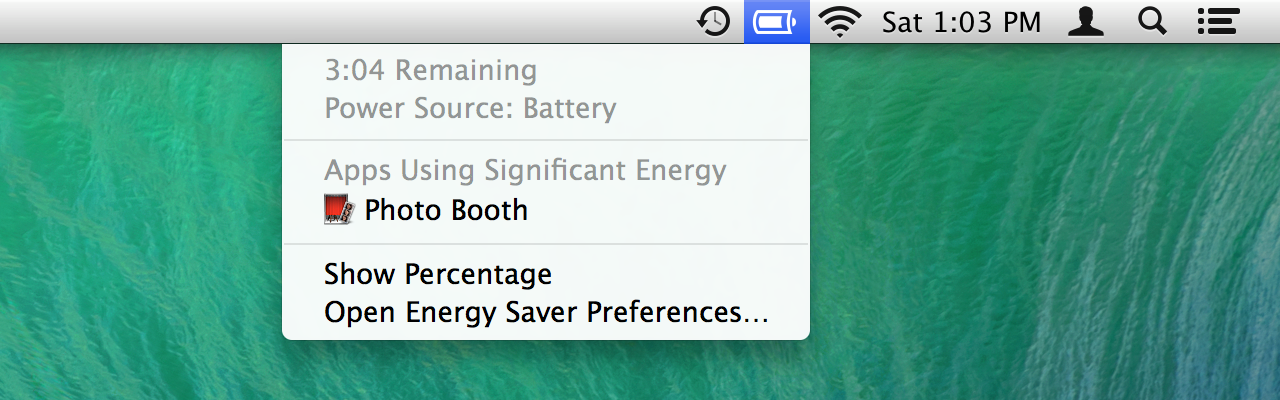
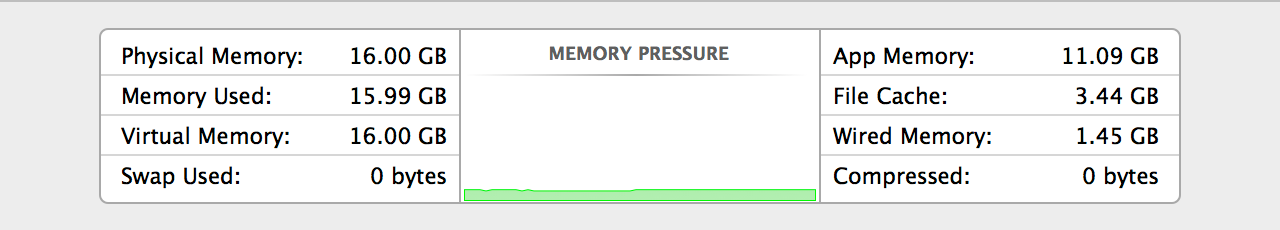
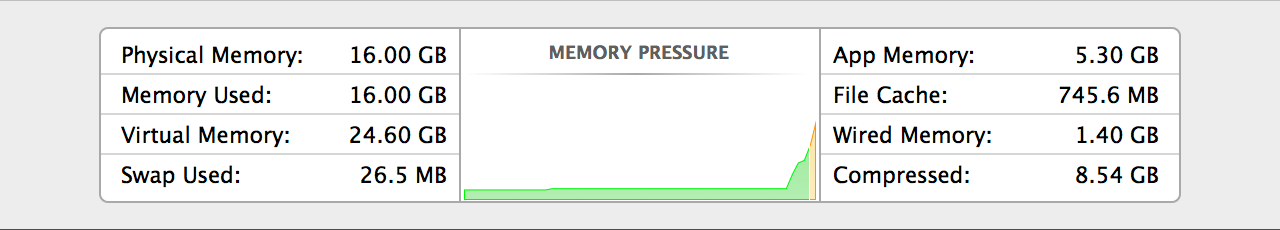



 Loading comments...
Loading comments...
